| Report Code: PP10235 | Published: May 2019 | Pages: 93 | Available format: |
| Therapeutic Area(s): | Oncology | Report Type: Epidemiology Insights and Forecast Reports |
Overview
Pancreatic cancer involves the development of malignant cells in the pancreas, resulting in the formation of tumor. The disease is further classified into two main groups: endocrine and exocrine tumors. Endocrine tumors, also known as islet cell tumors or neuroendocrine tumors, are less common and are mostly benign in nature. On the other hand, exocrine tumors or adenocarcinomas is a common type and forms in the pancreas ducts.
The disease has a poor prognosis and is rarely detected in its early stages due to lack of visibility of symptoms. Some of the risk factors associated with pancreatic cancer include diabetes, smoking, family history, obesity, age, and pancreatitis.
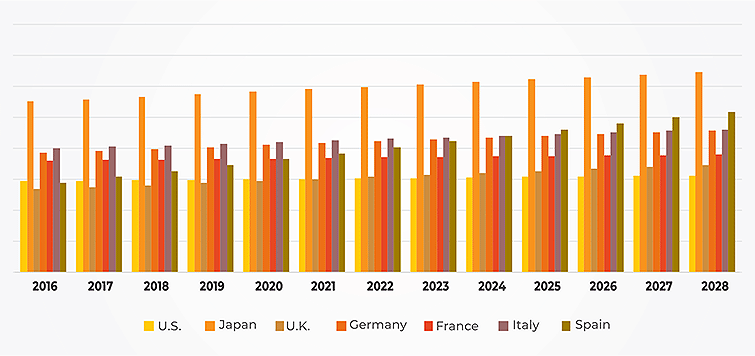
From the epidemiology point of view, pancreatic cancer in spite of arising as the 13th leading cancer worldwide, is on the path of becoming the fourth most common cause of death in the U.S. by 2020. The Departments of Oncology and Epidemiology in 2018 reported a slight but significant increase in survival rates from 4-5% to as high as 8% in the U.S. Moreover, lack of appropriate diagnosis, treatment and cataloging of cancer cases have led to increased mortality from this disease.
Pancreatic cancer is reported to be slightly more common in men as compared to women, mainly because men are more likely to smoke and thereby at a higher risk. Age is another significant risk factor of the disease and it has been observed that over 80% of pancreatic cancer cases develop between the age of 60 to 80 years.
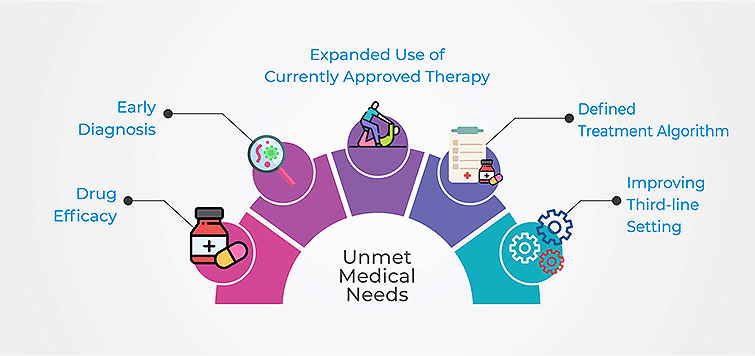
Unmet Medical Needs for Pancreatic Cancer
The report also covers some of the unmet medical needs responsible for the increasing incidence rate of pancreatic cancer and ineffective treatment of the patients. Over the past few decades, considerable progress has been marked in the treatment of patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. However, only a few drugs have been approved for this indication. The current marketed drugs have limited efficacy and there is a need to focus on improving the quality of therapeutic drugs:
Key Report Insights
The report provides detailed overview of pancreatic cancer, highlighting the causes, risk factors, classification, prognosis, pathophysiology, unmet medical needs, diagnosis, treatment options, and treatment algorithm for this disease. The report also provides comprehensive insights into global trends of pancreatic cancer in the 7MM. Moreover, pancreatic cancer incidence for historical and forecasted periods has been analyzed in-depth and is further segmented into age-specific, sex- specific, and stage-specific data.